Monitoring of radon concentration in enclosed spaces
Challenge
| For additional information about real-time monitoring system you can write us at radon@3-port.si. For ordering official measurement write at radon@zvd.si |
The earth’s crust naturally contains radionuclides, from which radon forms during the decay process. The most important is 222Rn (the radon isotope with the longest lifespan); it contributes to almost 90% of the inhaled radiation load. Radon is classified as a noble gas, is chemically inactive, and percolates from the soil towards the surface. It concentrates in enclosed spaces or exhales into the atmosphere. The concentration of radon in enclosed spaces can reach such high levels that the alpha radiation during a person’s life-span causes irreparable lung tissue cell mutations, the consequences of which can also be cancer.
The World Health Organisation (WHO) carried out an international project on the effects of radon from 2005 to 2007; experts from 30 different countries participated. It was concluded by the experts in the “WHO Handbook on Indoor Radon 2009” that epidemiological studies confirm that radon in the living area increases the possibility of lung cancer for the residents. They suggested that the annual average concentration of radon in the living area should be lower than 300 Bq/m3, which represents the effective dose of 10 mSv per year.
The International Commission on Radiological Protection ICRP in its publication “ICRP 126: Radiological Protection against Radon Exposure, 2014” suggested that the limit of radon concentration in the living environment should not exceed 300 Bq/m3 and should not exceed 1000 Bq/m3 in the working environment (see additional source for Slovenia: Institute for Occupational Safety/Laboratory for Physical Measurement’s report for 2016 (pdf).
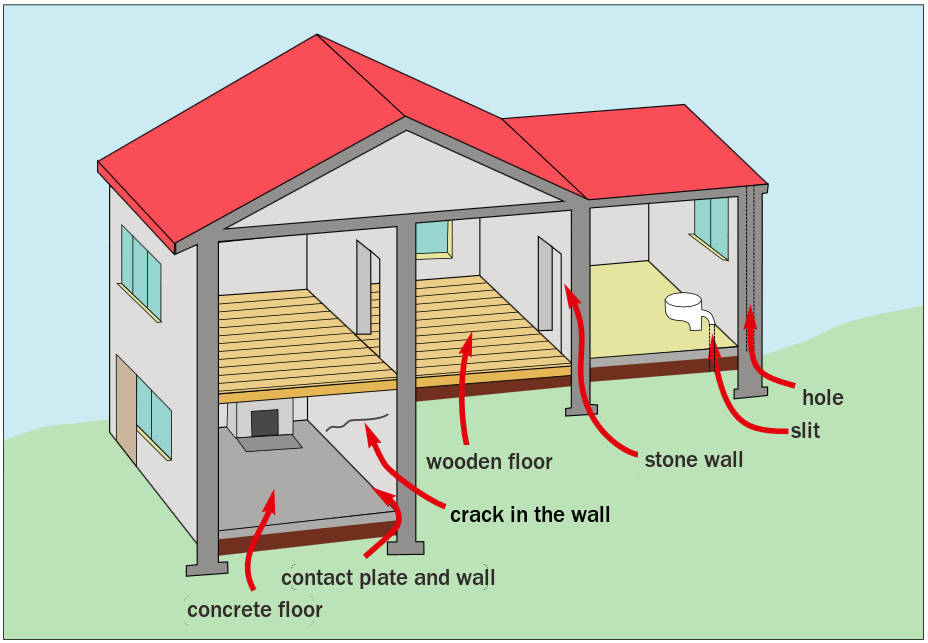
Radon penetrating from the ground to the building (source: publication Raopis, 2006)
The figure schematically shows the penetration of radon from the ground to the building (source: Raopis; June 2006), Publications of the Slovenian Radioactive Waste Agency ARAO). You can also read the short text about Radon (ion the site of the Slovenian Radiation Protection Administration.
Due to possible adverse effects of higher radon concentrations, especially on younger organisms, systematic examinations of living and working environments are required by law. By taking appropriate measures, the radon load can be significantly reduced. Measurements are conducted especially in areas, where we can expect that the annual average exceeds the reference limit, due to the geological composition of soil, tectonic fractures, and porous rocks.
 In Slovenia, the measurements are regularly conducted by certified Laboratory for Measuring Specific Radionuclide Activities. The measurements are conducted by installing passive or active measuring devices for a specific time period. According to the 2016 report (pdf), 953 radon concentration measurements were conducted between 2006 and 2016 in 444 facilities, of which 777 measurements were conducted in 393 schools and kindergartens, 155 measurements in 40 public institutions, and 21 measurements in 12 apartments. In 109 schools and kindergartens, as well as in 4 apartments, the radon concentration exceeded 400 Bq/m3, while in 16 other institutions the concentration exceeded 1000 Bq/m3.
In Slovenia, the measurements are regularly conducted by certified Laboratory for Measuring Specific Radionuclide Activities. The measurements are conducted by installing passive or active measuring devices for a specific time period. According to the 2016 report (pdf), 953 radon concentration measurements were conducted between 2006 and 2016 in 444 facilities, of which 777 measurements were conducted in 393 schools and kindergartens, 155 measurements in 40 public institutions, and 21 measurements in 12 apartments. In 109 schools and kindergartens, as well as in 4 apartments, the radon concentration exceeded 400 Bq/m3, while in 16 other institutions the concentration exceeded 1000 Bq/m3.
On December 12, 2017, the National Assembly of the Republic of Slovenia adopted the Ionising Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Act (ZVISJV-1, UL RS št. 76), which entered into force on December 22, 2017, and which in entirety replaced the existing law from 2002, which was last amended in 2015. The new law, which was co-written by the experts from the Slovenian Nuclear Safety Administration, is based on the latest findings from the radiological safety field, which are summarised in the ICRP’s reports (International Commission on Radiological Protection). These reports are acknowledged as radiological protection standards in almost every country and are acknowledged in the legal system.
The main changes brought forth by the new law concern the field of radiation protection due to natural sources of radiation, including radon protection in the working and living environment. The law also includes measures for reducing exposure from construction materials and informing, about the issue, all affected as well as stipulates obligatory systematic radon exposure measurements in the following areas:
- in facilities intended for the implementation of educational, cultural, or health programmes;
- in basement or ground floor living spaces or in other places where average annual concentrations of radon can be expected to exceed the reference levels;
- external exposures in enclosed spaces in existing facilities, due to the construction material used;
- exposure to radon in cases where a higher radon concentration can be expected, such as spas, caves, mines, and other underground spaces;
- at work places in areas with more radon. The employer’s obligation to provide measurements of radon in basement or ground floor workplaces is being implemented.
Regulation about a National Radon Programme, which shall determine the national reference levels of radon concentrations in the working and living environment, is being prepared (the EU Regulation states that the national reference level of the average annual radon concentration in the air in enclosed spaces must not exceed 300 Bq/m3).
The challenge we are trying to find a solution to is, how to, considering the management of long-term health risks due to radon exposure, enable all interested parties reliable, economically acceptable, and constant measurements in their environments.
Solution
There are various types of radon monitors, both passive and active. The prices may vary from a couple of hundred euros to over a thousand euros, depending on the measuring type and accuracy. In collaboration with researchers Damjan Šonc, PhD and Franci Henigman MSc, who developed an innovative, high-quality, and competitively priced radon monitor, the platform SMIP developed the dedicated software RADON Sense that compliments their radon monitor. It enables real-time logging of radon concentration data, which is sent by the sensor to the cloud. The sample gauge has obtained the calibration certificate of the accredited laboratory BFS Radon-Kalibrielaboratorium in Berlin.
The standard version of the meter is intended for use in rooms where humidity does not condense (relative humidity below 95%). The following communication links are currently provided: RS485, Ethernet, WiFi, LoRa, and power options include: external power supply, POE and battery power (LoRa communication only).

Radon Sensor
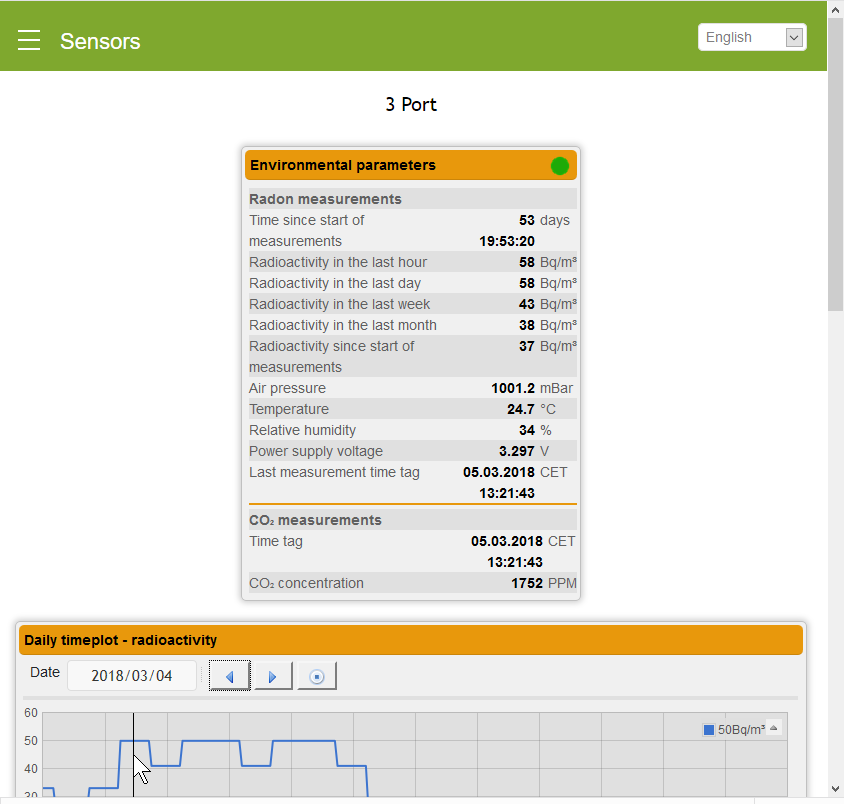
The RADON Sense’s Dashboard (SMIP platform software)
The RADON Sense app displays hourly measurement as well as daily, monthly, and yearly averages. App extensions for notifying specified e-mail addresses and long-term data storage are planned. If the data is stored, the history of measurements is displayed in graphs.
Results
RADON Sense’s key advantage is that the registered user has the option of real-time remote access to the current measurements via the internet, in all locations, where the radon monitors are installed.
By installing one or more radon monitors, especially in the basement and ground floor spaces, we can provide all interested schools, kindergartens, public institutions, companies, floor owners, users of residential housing units, etc. an easy solution that allows regular monitoring of radon concentration and therefore the chance to take early action in the spaces where the concentrations are elevated or where the reference values are exceeded.
Measures for reducing the exposure are diverse. They vary from simple measures, such as
- ventilating spaces,
- relocating staff to other spaces,
- stopping regular use of spaces,
- reorganising work tasks and working hours
to more permanent measures, such as filling cracks and other construction work if exposure to radon cannot be reduced by simpler measures. One possible measure is to collaborate with an appropriately certified institution, which owns measuring instruments and educated staff to conduct extremely accurate measurements and which can provide an expert interpretation of results. Such extremely accurate measurements are sometimes necessary to determine the exact micro-locations (cracks, openings, terminals) from where radon penetrates into the enclosed space, before any repair work can be done.
|
For more informations about RADON Sense system write us at radon@3-port.si. By adding new sensors for environmental parameters we expanded the RADON Sense application functionalities to new application SMIP Sense. |


